9. Cascade Plugins¶
Django-SHOP extends the used eco-system arround django-CMS plugins, djangocms-cascade, by additional shop-specific plugins. This allows us to create a whole shopping site, which consists of many different elements, without having to craft templates by hand – with one exception: The product detail views.
Therefore all we have to focus on, is a default page template with one big placeholder. This placeholder then is subdivided into containers, rows, columns and other elements of the Cascade plugin collection.
This however requires a completely different approach, from a designer’s point of view. The way web design has been done a few years ago, starting with the screenshot of a finished page, must be rethought. This has been discussed in length by many web-designers, especially by Brad Frost in his excellent book on Atomic Web Design. He propagates to reverse the design process and start with the smallest entity, which he calls Atoms. They form to bigger components, named Molecules, which themselves aggregate to Organisms.
Some designers nowadays build those components directly in HTML and CSS or SASS, instead of drawing their screens using programs such as InDesign or PhotoShop (which by the way never was intended for this kind of work). It also exempts having the programmer to convert those screens into HTML and CSS – a time consuming and unsatisfying job.
According to Frost, the next bigger component after the Organism is the template. This is where djangocms-cascade jumps in. Each of the Cascade plugins is shipped with its own default template, which can easily be overwritten by the designers own implementation.
9.1. Overriding Templates¶
For all plugins described here, we can override the provided templates with our own implementation.
If the shop framework provides a template, named /shop/folder/my-organism.html, then we may
override it using /merchantimplementaion/folder/my-organism.html.
This template then usually extends the existing framework template with
{% extends "/shop/folder/my-organism.html" %}
{% block shop-some-identifier %}
<div>...</div>
{% endblock %}
This is in contrast to Django’s own implementation for searching the template, but allows to extend exiting templates more easily.
9.2. Breadcrumb¶
The BreadcrumbPlugin has four different rendering options: Default, Soft-Root, With Catalog Count and Empty. It can be added exclusively to the placeholder named Breadcrumb, unless otherwise configured.
The Default breadcrumb behaves as expected. Soft-Root appends the page title to the existing breadcrumb, it shall be used for pages marked as soft root. A breadcrumb of type With Catalog Count adds a badge containing the number of items. Use an Empty to hide the breadcrumb otherwise displayed by the placeholder as default.
9.3. Cart¶
The CartPlugin has four different rendering options: Editable, Static, Summary and Watch-List. Refer to the Cart using a Cascade Plugin for details.
9.4. Checkout Forms¶
All Forms added to the checkout page are managed by members of the Cascade plugin system. All these
plugin inherit from a common base class, shop.cascade.plugin_base.DialogFormPluginBase.
They all have in common to render and validate one specific Form, which itself inherits from
shop.forms.DialogForm or shop.forms.DialogModelForm.
A nice aspect of this approach is, that …
- if we add, change or delete attributes in a form, fields are added, changed or deleted from the rendered HTML as well.
- we get client side form validation for free, without having to write any Javascript nor HTML.
- if we add, change or delete attributes in a form, this modification propagates down to both form validation controllers: That one in Javascript used on the client as well as the final one, validating the form on the server.
- if our forms are made out of models, all of the above works as well.
- we can arrange each of those form components using the Structure editor from django-CMS toolbar. This is much faster, than by crafting templates manually.
As we can see from this approach, django-SHOP places great value on the principles of a Single Source of Truth, when working with customized database models and forms.
Many of these Forms can be rendered using two different approaches:
9.4.1. Form dialog¶
Here we render all model fields as input fields and group them into an editable form. This is the normal use case.
9.4.2. Static summary¶
Here we render all model fields as static strings without wrapping it into a form. This shall be used to summarize all inputs, preferably on the last process step.
These are the currently available plugins provided by django-SHOP to build the checkout page:
9.4.2.1. Customer Form Plugin¶
The Customer Form is used to query information about some personal information, such as
the salutation, the first- and last names, its email address etc. In simple terms, this form
combines the fields from the model classes shop.models.customer.Customer and
email_auth.models.User or auth.models.User respectively. This means that fields,
we add to our Customer model, are reflected automatically into this form.
9.4.2.2. Guest Form Plugin¶
The Guest Form is a reduced version of the Customer Form. It only asks for the email address, but nothing else. We use it for customers which do not want to create an account.
9.4.2.3. Shipping- and Billing Address Forms¶
There are two form plugins, where customers can add their shipping and/or billing address. The
billing address offers a checkbox allowing to reuse the shipping address. By overriding the form
templates, this behavior can be switched.
Both plugins provide a form made up from the model class implementing
shop.models.address.AddressModel.
9.4.2.4. Select the Payment Provider¶
For each payment provider registered within django-SHOP, this plugin creates a list of radio buttons, where customers can choose their desired payment provider. By overriding the rendering templates, additional forms, for instance to add credit card data, can be added.
9.4.2.5. Select a Shipping Method¶
For each shipping provider registered within django-SHOP, this plugin creates a list of radio buttons, where customers can choose their desired shipping method.
9.4.2.6. Extra Annotations Plugin¶
This plugin provides a form, where customers can enter an extra annotation, while they proceed through the checkout process.
9.4.2.7. Accept Condition Plugin¶
Normally customers must click onto a checkbox to accept various legal requirements, such as the terms and conditions of this site. This plugin offers a text editor, where the merchant can enter a paragraph, possibly with a link onto another CMS page explaining them in more details.
9.4.2.8. Required Form Fields Plugin¶
Most checkout forms have one or more required fields. To labels of required input fields, an asterisk is appended. This plugin can be used to add a short text message stating “* These fields are required”. It normally should be placed between the last checkout form and the proceed button.
9.4.2.9. Proceed Button¶
This plugin adds a styleable proceed button to any placeholder. This kind of button differs from a clickable link button in that sense, that it first sends all gathered form data to the server and awaits a response. Only if all forms are successfully validated, this button proceeds to the given link.
This proceed button can also handle two non-link targets: “Reload Page” and “Purchase Now”.
The first target is useful to reload the page in a changed context, for instance if a site visitor logged in and now shall get a personalized page.
The second target is special to django-SHOP and exclusively used, when the customer performs The Purchasing Operation.
9.5. Authentication¶
Before proceeding with various input forms, we must know the authentication status of our site visitors. These different states are explained here in detail: Anonymous Users and Visiting Customers.
Therefore we need pluggable forms, where visitors can sign in and out, change and rest passwords and so on. All this authentication forms are handled by one single plugin
9.5.1. Authentication Plugin¶
This plugin handles a bunch of authentication related forms. Lets list them:
9.5.2. Login Form¶
This is a simple login form accepting a username and password.
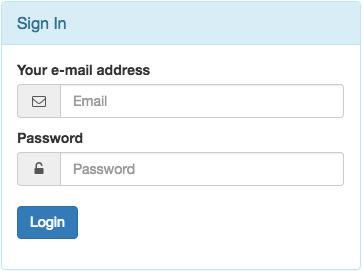
This form normally is used in combination with Link type: CMS Page.
9.5.3. Logout Form¶
This logout form just adds a button to sign out from the site.
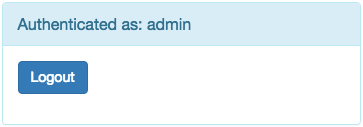
This form normally is used in combination with Link type: CMS Page.
9.5.5. Password Reset Form¶
This form offers a field, so that registered users, which forgot their password, can enter their email address to start a password reset procedure.
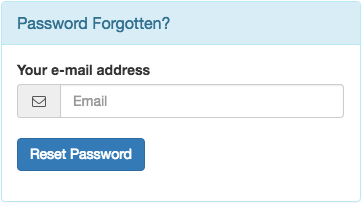
9.5.6. Login & Reset Form¶
This extends the Shared Login/Logout Form by combining it with the Password Reset Form form.
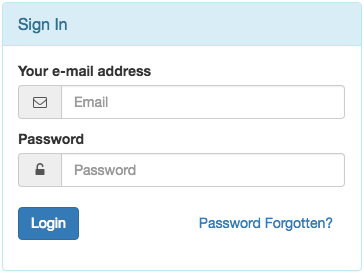
If someone clicks on the link Password Forgotten? the form extends to
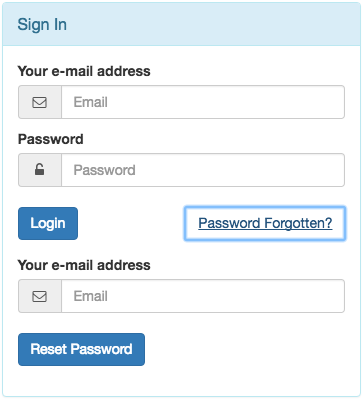
This form normally is used in combination with Link type: Reload Page.
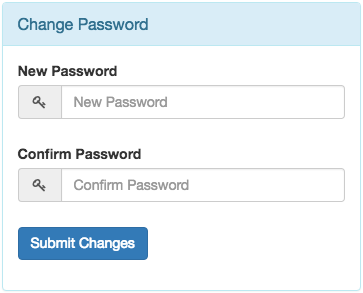
9.5.7. Change Password Form¶
This form offers two field to change the password. It only appears for logged in users.
9.5.8. Register User Form¶
Using this form, anonymous visitors can register themselves. After having entered their email address and their desired passwords, they become registered users.
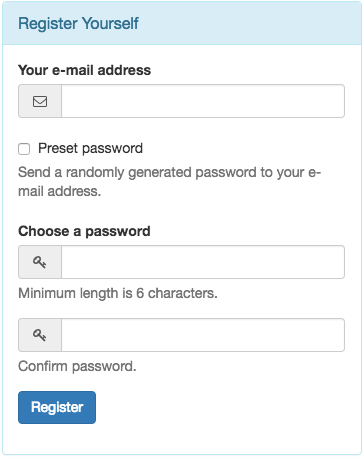
This form normally is used in combination with Link type: Reload Page.
9.5.9. Continue as Guest Form¶
This form just adds a button, so that visitors can declare themselves as guest users who do not want to register an account, nor expose their identity.
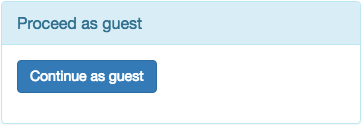
This form normally is used in combination with Link type: Reload Page.
9.6. Process Bar¶
The ProcessBarPlugin can be used to group many forms plugins onto the same page, by dividing them up into different block. Only one block is visible at a time. At to top of that page, a progress bar appears which shows the active step.
This plugin checks the validity of all of its forms and allows to proceed to the next step only, if all of them are valid.
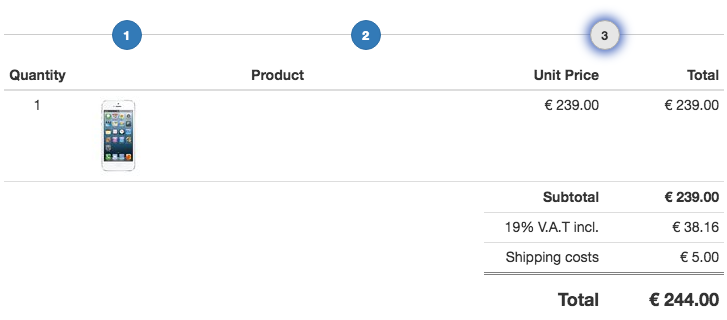
Each step in that process bar must contain a Next Step Button, so that the customer can move to the next step, provided all forms are valid.
The last step shall contain a Proceed Button which shall be configured to take appropriate action, for instance to start the purchasing operation using the Link type “Purchase Now”.
Note
This plugin requires the AngularJS directive <bsp-process-bar> as found in the
npm package angular-bootstrap-plus.
9.7. Catalog¶
The catalog list view is handled by the ShopCatalogPlugin.
This plugin requires a CMS page, which uses the apphook ProductsListApp. First assure that we Create the CatalogListApp. This CMSapp must be implemented by the merchant; it thus is part of the project, rather than the django-SHOP framework.
9.8. Viewing Orders¶
The Order Views plugin is used to render the list- and detail views of orders, specific to the currently logged in customer. Without a number in the URL, a list of all orders belonging to the current customer is shown. By adding the primary key of a specific order to the URL, all ordered items from that specific order are shown. We name this the order detail view, although it is a list of items.
This plugin requires a CMS page, which as uses the CMSApp OrderApp. This CMS application is part of the shop framework and always available in the Advanced Settings of each CMS page.
9.8.1. Caveat when editing the Order Detail Page¶
The Order List- and Detail Pages share one common entity in our CMS page tree. The Order Detail view just rendered in a different way. Editing this pseudo page therefore is not possible because it is not part of the CMS.
9.9. Search Results¶
Rendering search results is handled by the Search Results plugin.
On a site offering full-text search, add a page to display search results. First assure that we have a Search View assigned to that page as apphook. This CMSapp must be implemented by the merchant; it thus is part of the project, rather than the django-SHOP framework.